Improving Mental Health: Does Psilocybin Help Treat Depression?
Depression casts a long shadow over the lives of millions worldwide, affecting not only the individuals who suffer from it but also their loved ones and communities. Despite advancements in mental health treatment, conventional treatments like medication and therapy may not always provide satisfactory results.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in alternative treatments, including the use of psilocybin, a naturally occurring compound found in certain mushrooms. This article explores the potential of psilocybin therapy as a novel approach to treating depression, shedding light on its efficacy, safety, and integration into depression treatment plans.
Understanding Depression
Depression, often characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest, is a complex and multifaceted mental health condition. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), depression is the leading cause of disability worldwide, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds. It can have profound effects on an individual’s daily functioning, relationships, and overall quality of life.
Depression encompasses a wide spectrum of symptoms, ranging from mild to severe, and can manifest differently in each individual. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent feelings of sadness or emptiness
- Loss of interest or pleasure in activities once enjoyed
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Sleep disturbances (insomnia or hypersomnia)
- Fatigue or loss of energy
- Feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Thoughts of death or suicide
While mild depression can be treated with drugs and therapy, these therapies are often ineffective in chronic cases. This is where psilocybin treatment steps in. Psilocybin interacts with the serotonin receptors in the brain to promote neuroplasticity and foster new positive perspectives in the brain. According to a study done by Johns Hopkins Medicine, regulated ingestion of psilocybin shows promising results in alleviating the impact of chronic depression.
Current Treatment Approaches
Treatment for depression typically involves a combination of medication, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes. Antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), are commonly prescribed to alleviate symptoms of depression by bringing the neurotransmitters in the brain back in balance.
Psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and interpersonal therapy (IPT), aims to help individuals by identifying and addressing negative thought patterns, developing coping strategies, and improving interpersonal relationships. Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, healthy diet, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques also play a significant role in controlling depression.
While these conventional treatments are effective for some people suffering from mild to medium-intensity depression, the treatments fail to deliver satisfactory results in cases of embedded and chronic depression. Furthermore, the drugs prescribed for depression can sometimes have adverse side effects, including blurred vision, confusion, and erectile dysfunction. As a result, there is a growing need for alternative and natural approaches that offer greater efficacy without the side effects.
Introduction to Psilocybin
Psilocybin is a naturally occurring compound found in certain species of mushrooms, colloquially known as “magic mushrooms” or “psychedelic mushrooms.” These mushrooms have been used for centuries in various cultural and spiritual practices, often revered for their hallucinogenic properties and purported therapeutic effects.
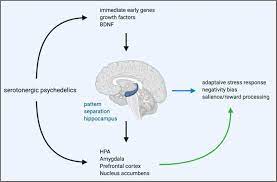
Psilocybin exerts its psychoactive effects by binding to serotonin receptors in the brain, particularly the 5-HT2A receptors. This leads to alterations in perception, mood, and cognition and helps break the negative thought cycle of depression. Historically, indigenous cultures in regions such as Mesoamerica and the Amazon have utilized psilocybin-containing mushrooms in religious ceremonies, healing rituals, and spiritual quests.
Research on Psilocybin and Depression
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of scientific interest in the therapeutic potential of psilocybin, particularly in the treatment of depression and other mental health conditions. A growing body of research has published results pointing to the underlying property of psilocybin as an antidepressant and as a novel and promising remedy for chronic depression.
Studies have shown that psilocybin therapy may produce rapid and sustained reductions in depressive symptoms, even in individuals who have not responded to conventional treatments. Research results published in the New England Journal of Medicine demonstrated promising results, with participants reporting significant improvements in mood, outlook on life, and overall well-being following psilocybin-assisted therapy sessions. Let’s look at some hard data.
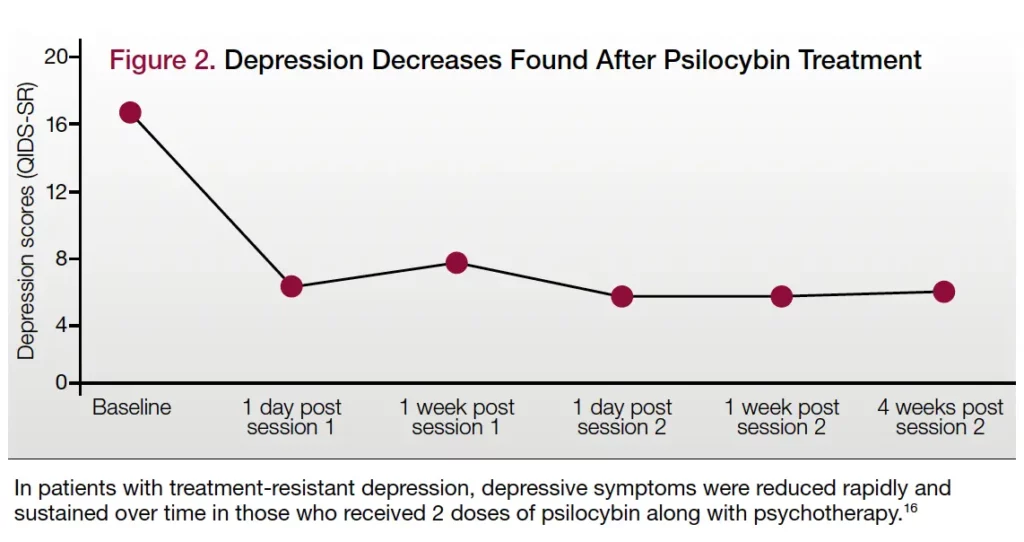
The graph above collates the findings of multiple studies on the effect of psilocybin on depression. On the Y-axis you have the Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology (QIDS) score that runs from 0-27. The score is calculated based on answers to a set of questions, and a final score of 0-5 rules out depression, while 16-20 indicates severe depression and 21-27 indicates very severe depression. The X-axis represents the time period of treatment. As shown, the first session brings the score down to around five, and the second session sustains the benefits even after four weeks.
A landmark study published in the Journal of Psychopharmacology found that a single dose of psilocybin, combined with psychotherapy, produced significant reductions in depression and anxiety symptoms in patients, and these effects were sustained for up to six months post-treatment, suggesting the potential for long-lasting therapeutic benefits.
Benefits of Psilocybin Therapy
The therapeutic benefits of psilocybin therapy extend beyond symptom relief to include profound psychological insights, emotional healing, and spiritual experiences. Many individuals undergoing psilocybin-assisted therapy report a sense of connection with themselves, others, and the natural world, as well as a newfound appreciation for life and its possibilities.
One of the unique aspects of psilocybin therapy is its ability to induce mystical or transcendent experiences characterized by a sense of unity, interconnectedness, and profound awe. These experiences, often described as “peak” or “transcendental” moments, have been associated with positive changes in attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, as well as enhanced well-being and life satisfaction.
Psilocybin therapy may also facilitate emotional processing and resolution of unresolved traumas or psychological conflicts, allowing individuals to confront and integrate difficult emotions or experiences in a safe and supportive environment. This process of “psychedelic therapy” is guided by trained therapists or facilitators who provide personalized support and guidance throughout the session.
Safety and Considerations
While psilocybin therapy shows promise as a treatment for depression, it is essential to recognize the potential risks and considerations associated with its use. Psilocybin is a potent psychoactive substance that can induce intense and unpredictable experiences, including anxiety, paranoia, and psychosis, particularly in vulnerable individuals or unsupervised settings.
Psilocybin therapy should only be administered under the guidance of trained professionals in a controlled clinical setting, where appropriate screening, preparation, and integration protocols can be implemented to ensure safety and efficacy. Patients with a history of psychiatric disorders, substance abuse, or cardiovascular complications may not be suitable candidates for psilocybin therapy.
Additionally, psilocybin therapy is not without potential adverse effects, which may include nausea, vomiting, increased heart rate, and transient changes in blood pressure. These side effects are typically mild to moderate in severity and tend to resolve spontaneously as the effects of psilocybin wear off.
Integrating Psilocybin into Depression Treatment
The integration of psilocybin therapy into depression treatment plans requires a collaborative and multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals, therapists, and patients. Before considering psilocybin therapy, individuals should undergo a thorough assessment to evaluate their suitability for treatment and address any potential risks or concerns.
During psilocybin therapy sessions, patients are encouraged to adopt an open and receptive mindset, allowing them to explore their inner experiences and emotions without judgment or resistance. Therapists provide a safe and supportive environment for patients to navigate the psychedelic experience, offering guidance, reassurance, and encouragement as needed.
After the session, patients participate in integration sessions, where they have the opportunity to reflect on their experiences, process their insights, and integrate them into their daily lives. Integration therapy aims to facilitate lasting changes in attitudes, behaviors, and beliefs, helping patients derive meaning and purpose from their psychedelic experiences.
Personal Testimonials
The potential of psilocybin therapy to transform lives and alleviate suffering is perhaps best illustrated by the personal testimonials of individuals who have undergone treatment for depression. Countless accounts from patients, therapists, and researchers attest to the profound and often life-changing effects of psilocybin therapy, offering hope and inspiration to those in need.
Many individuals describe their experiences with psilocybin therapy as deeply transformative, resulting in profound shifts in perception, consciousness, and self-awareness. Some report breakthrough insights into long-standing psychological issues or traumas, while others describe feelings of profound love, connection, and unity with themselves, others, and the universe.
Conclusion
In conclusion, psilocybin therapy holds considerable promise as a novel and potentially transformative treatment for depression, offering new hope for individuals who have not responded to conventional therapies. While research is still ongoing, the existing evidence suggests that psilocybin therapy may offer a valuable addition to the arsenal of treatments for depression.
As we continue to explore the therapeutic potential of psilocybin and other psychedelics, it is essential to approach this field with humility, curiosity, and scientific rigor. By harnessing the power of psychedelics in a responsible and ethical manner, we may unlock new avenues for healing, growth, and self-discovery, ultimately leading to a brighter future for mental health treatment.
Q&A
- Q: How does psilocybin help alleviate symptoms of depression?
A: Psilocybin interacts with serotonin receptors in the brain, leading to altered brain activity and mood regulation. It promotes neuroplasticity and fosters new perspectives, potentially breaking negative thought patterns associated with depression.
- Q: Are the effects of psilocybin therapy long-lasting in treating depression?
A: Research suggests that a single dose of psilocybin, combined with therapy, can produce significant and enduring reductions in depressive symptoms. These effects can last for weeks to months, offering prolonged relief from depression.
- Q: What makes psilocybin therapy unique compared to traditional antidepressants?
A: Psilocybin therapy offers a novel approach by addressing the root causes of depression through profound introspection and emotional processing. Unlike traditional antidepressants, which primarily target symptoms, psilocybin therapy can lead to transformative insights and lasting behavioral changes.
- Q: Is psilocybin therapy safe for individuals with depression?
A: Psilocybin therapy should only be administered under the guidance of trained professionals in a controlled clinical setting. While generally well-tolerated, psilocybin can induce intense psychological experiences that may be challenging for some individuals. Proper screening, preparation, and integration are essential to ensure safety and efficacy.
- Q: Can psilocybin therapy benefit individuals who have not responded to conventional treatments for depression?
A: Yes, psilocybin therapy shows promise for treatment-resistant depression, offering new hope for individuals who have not found relief with traditional antidepressants or therapy. Its unique mechanism of action and ability to induce profound psychological insights make it a valuable addition to the treatment landscape for depression.
Call to Action
The mushroom industry is at a turning point. As leaders, it’s up to us to act on what we know about the mushroom life cycle, sustainable farming, and technology. Let’s prioritize sustainable practices like reducing water usage and waste, not only for the planet but also for cost savings. Embrace technology like AI and automation to optimize cultivation and meet market demands for organic and sustainable produce. This is our chance to shape the future of mushroom cultivation—let’s make it sustainable, innovative, and ethical. This article was brought to you by the good folks at Royal Mycology. Check out our Instagram page for more details
References
- Carhart-Harris, R. L., & Goodwin, G. M. (2017). The therapeutic potential of psychedelic drugs: Past, present, and future. Neuropsychopharmacology, 42(11), 2105–2113.
- Griffiths, R. R., et al. (2016). Psilocybin produces substantial and sustained decreases in depression and anxiety in patients with life-threatening cancer: A randomized, double-blind trial. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 30(12), 1181–1197.
- Johnson, M. W., & Griffiths, R. R. (2017). Potential therapeutic effects of psilocybin. Neurotherapeutics, 14(3), 734–740.
- Nichols, D. E., & Johnson, M. W. (2019). Psilocybin: From ancient magic to modern medicine. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 33(9), 1088–1108.